अधिवृषण
अधिवृषण या एपिडिडीमिस (epididymis) पुरुष जनन तंत्र की वह नलिका है जो अण्डकोश (testicle) को शुक्रवाहिका (vas deferens) से जोड़ती है। अधिवृषण सभी नर सरीसृपों, पक्षियों, और स्तनधारियों में पाया जाता है। वयस्क पुरुषों में यह ६ से ७ मीटर लम्बी, पतली, पास-पास कुण्डलित एकल नलिका होती है।[1]
| अधिवृषण | |
|---|---|
 वयस्क मानव का वृषण, अधिवृषण के साथ: A. अधिवृषण शीर्ष, B. अधिवृषण का मुख्य भाग, C. अधिवृष्ण पुच्छ, तथा D. शुक्रवाहिका | |
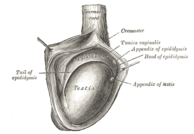 The right testis, exposed by laying open the tunica vaginalis. | |
| विवरण | |
| लातिनी | Epididymis |
| अग्रगामी | Wolffian duct |
| Pampiniform plexus | |
| अभिज्ञापक | |
| NeuroNames | {{{BrainInfoType}}}-{{{BrainInfoNumber}}} |
| टी ए | A09.3.02.001 |
| एफ़ एम ए | 18255 |
| शरीररचना परिभाषिकी | |
संरचना संपादित करें
अधिवृषण के तीन भाग होते हैं-
- शीर्ष (लातिन: caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinium of the testis. It is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle.[2] It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentrated. The concentration of the sperm here is dilute.
सन्दर्भ संपादित करें
- ↑ Kim, Howard H.; Goldstein, Marc (2010). "Chapter 53: Anatomy of the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicle". प्रकाशित Graham, Sam D.; Keane, Thomas E.; Glenn, James F. (संपा॰). Glenn's urological surgery (7th संस्करण). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. पृ॰ 356. आई॰ऍस॰बी॰ऍन॰ 978-0-7817-9141-0.
- ↑ अ आ इ Bacha, William; Bacha, Linda (2012). Color Atlas of Veterinary Histology. Wiley-Blackwell. पृ॰ 226. आई॰ऍस॰बी॰ऍन॰ 0470958510.